
Book a Free Consultation Now
Would you like to know more about this topic?
Contact us on WhatsApp and get a free consultation from our experts
Contact on WhatsApp NowTo learn How to disavow malicious links, you must first audit your backlinks, identify toxic or manipulative links, attempt manual removal, then submit those links in a properly formatted disavow file through Google Search Console. This process helps Google ignore harmful backlinks and protects your website from penalties. At Nofal SEO, we handle link disavowal with expert analysis and manual review to ensure only truly dangerous links are disavowed, safeguarding your SEO performance and long-term growth.
What Is Link Disavowal?
Link disavowal is an advanced SEO practice used to protect a website from harmful backlinks that may negatively influence search engine rankings. When discussing How to disavow malicious links, the concept centers on informing Google that certain inbound links should be ignored during ranking evaluation. These links usually originate from spammy websites, link farms, hacked domains, or automated networks that violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. If left untreated, such backlinks can weaken a site’s authority and, in severe cases, trigger manual or algorithmic penalties.
From a broader SEO perspective, link disavowal plays a corrective—not proactive—role. It supports backlink profile cleanup and reinforces Google penalty prevention by allowing search engines to reassess your site without the influence of toxic signals. Disavowal should never be used casually; instead, it acts as a safeguard when manual link removal is impossible or ineffective, especially in cases of negative SEO or legacy black-hat link building.
Before diving into the practical steps, it’s important to understand how link disavowal works in real SEO scenarios and why misuse can be just as harmful as ignoring toxic links.
-
Link disavowal does not remove links physically
The links remain live on external websites, but Google is instructed to discount them when assessing your site. This distinction is critical because many site owners mistakenly believe disavowal deletes backlinks, which can lead to unrealistic expectations. -
It is designed for links you cannot control
Disavowal is mainly used when you have no authority over the linking domain, such as spam blogs, auto-generated directories, or malicious websites that refuse removal requests. -
It protects ranking signals rather than boosting rankings directly
Disavowing links does not improve rankings instantly. Instead, it prevents further damage and allows your website’s legitimate authority signals to perform without interference. -
Incorrect disavowal can harm SEO performance
Disavowing healthy or neutral links by mistake can reduce link equity, slow down growth, and weaken your backlink profile over time.
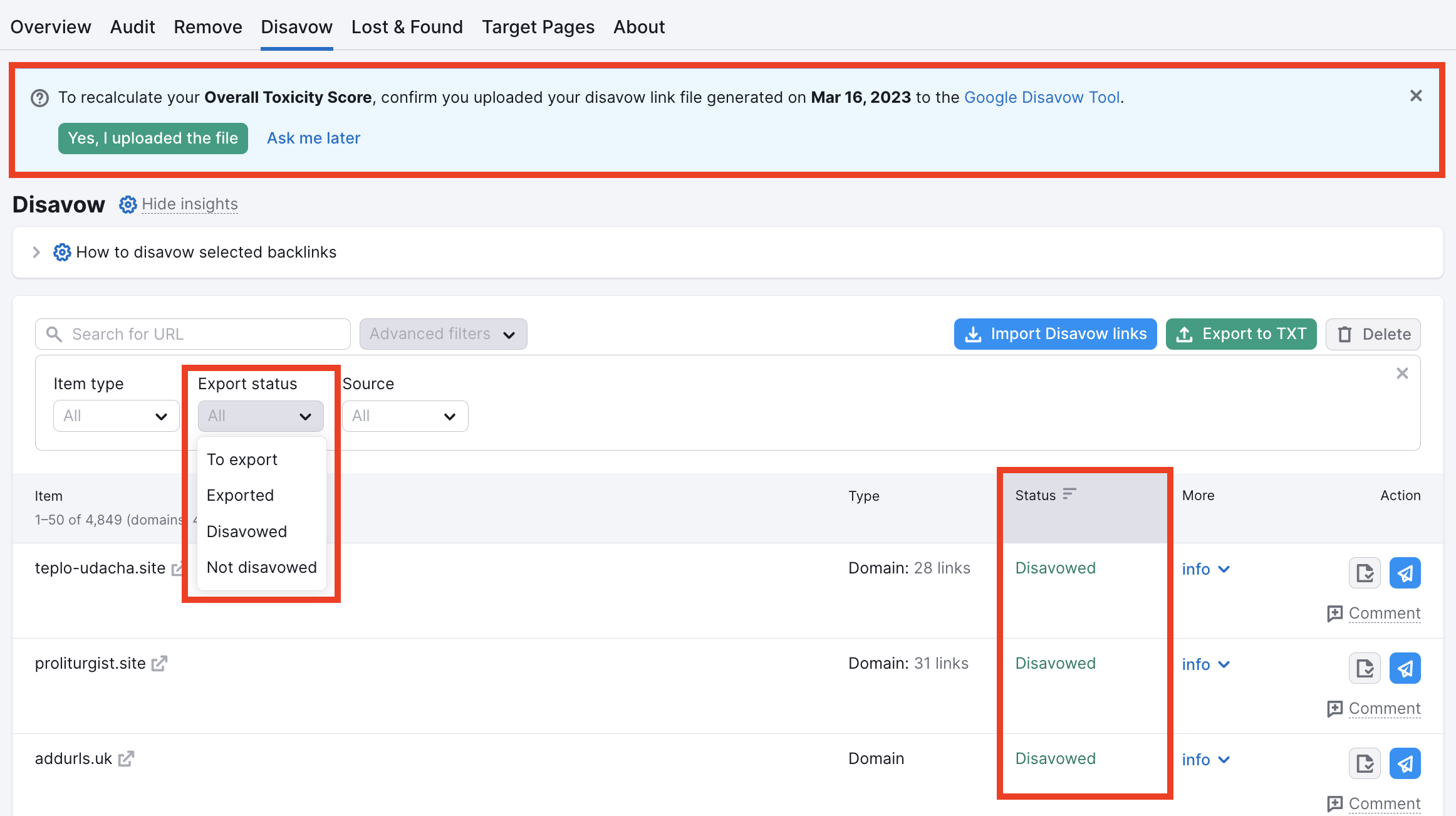
What’s the Disavow Tool?
The Disavow Tool is a specialized feature provided by Google that allows website owners to submit a list of URLs or domains they want Google to ignore. In the context of How to disavow malicious links, this tool acts as the official communication channel between webmasters and Google’s ranking systems regarding harmful backlinks. It is primarily accessed through Google Search Console and is intended for advanced SEO use only.
From an operational standpoint, the Disavow Tool supports manual action recovery and toxic backlink mitigation by enabling Google’s algorithms to reevaluate a website without counting disavowed links. However, Google itself has stated that the tool should be used cautiously and only when there is a clear pattern of unnatural or manipulative links that cannot be resolved through manual outreach.
To properly use the Disavow Tool, you need to understand its purpose, limitations, and the risks associated with incorrect implementation.
-
The tool works by processing a disavow file
You upload a text file listing the links or domains you want ignored. Google then gradually incorporates this information as it recrawls and reassesses those backlinks. -
It is not a shortcut for fixing poor SEO practices
The Disavow Tool cannot compensate for weak content, poor site structure, or ongoing black-hat link building. It only addresses external link risks. -
Google may already ignore some spam links automatically
This means the tool is most useful when spam links are excessive, manipulative, or directly associated with penalties—not for every low-quality backlink. -
Once submitted, disavowal effects are not immediate
Results depend on crawl frequency, link volume, and algorithm updates, which is why disavowal should be monitored over weeks or months.

When Should You Disavow Links?
Knowing when to take action is just as important as knowing how to do it, because disavowing links at the wrong time can cause more harm than benefit. The core idea behind How to disavow malicious links is risk management, not routine cleanup. Disavowal should be used only when toxic backlinks pose a real threat to your site’s visibility, credibility, or compliance with search engine guidelines. Many websites rank well despite having some low-quality links, which means disavowal is not always necessary.
From a strategic SEO perspective, disavowing links is usually tied to manual penalties or algorithmic suppression caused by unnatural link patterns. If your site has experienced sudden ranking drops, indexing issues, or received a manual action notice, this is when disavowal becomes relevant. Otherwise, preemptive disavowing without evidence of harm can weaken your backlink profile unnecessarily.
Before deciding to disavow, it’s important to recognize the warning signs that justify taking this step.
-
You have received a manual action related to unnatural links
This is the clearest signal that disavowal is required. In such cases, Google explicitly indicates that certain backlinks are violating its guidelines, making disavowal a critical part of recovery. -
There is a clear pattern of manipulative or spam-based backlinks
If backlinks come from link farms, auto-generated blogs, or irrelevant foreign domains at scale, this suggests intentional or malicious linking behavior that should be addressed. -
Negative SEO attacks are affecting your site
In some industries, competitors may point spam links to your website intentionally. Disavowal helps neutralize this threat when link removal is not possible. -
Manual removal attempts have failed
Disavowal should always come after outreach. If webmasters ignore or refuse link removal requests, disavowing becomes the fallback solution.
How to Disavow Malicious Links
Step 1: Audit Your Backlink Profile
Start by collecting all your backlinks using reliable SEO tools and Google Search Console. Review the links carefully to identify spammy, irrelevant, or manipulative domains that could harm your site’s SEO performance.
Step 2: Identify Truly Malicious Links
Analyze each suspicious link based on domain quality, relevance, anchor text, and linking patterns. Focus on links coming from link farms, hacked sites, automated blogs, or unrelated niches, and avoid labeling neutral or natural links as toxic.
3: Attempt Manual Link Removal
Before disavowing, try contacting website owners and request link removal. Document all outreach attempts, as Google prefers manual cleanup before using the disavow option.
Step 4: Create a Disavow File
Prepare a plain text (.txt) file listing the malicious URLs or entire domains you want Google to ignore. Use proper formatting, add comments if needed, and double-check for errors to avoid disavowing valuable links.
5: Submit the Disavow File to Google
Upload the disavow file through Google Search Console’s Disavow Tool. Once submitted, Google will gradually process the file as it recrawls the listed links.
Step 6: Monitor Results Over Time
Track your rankings, organic traffic, and manual action status. Disavowal does not work instantly, so allow several weeks or months for Google to reassess your backlink profile.
How Do I Identify Toxic Backlinks?
Identifying toxic backlinks requires more than relying on automated scores or tools; it demands contextual SEO judgment. When applying How to disavow malicious links, toxicity is determined by link intent, relevance, and quality—not just domain authority. A link from a low-traffic site is not automatically toxic, while a high-authority site engaging in manipulative linking can still be harmful.
Professionally, toxic link identification involves combining backlink audits with manual link evaluation. This process looks at anchor text patterns, linking domain behavior, topical relevance, and historical spam indicators. The goal is to isolate links that actively distort your site’s link profile rather than those that are simply neutral.
To properly identify toxic backlinks, several evaluation layers must be applied.
-
Analyze anchor text distribution carefully
Overuse of exact-match commercial keywords is one of the strongest toxicity indicators. Natural backlinks usually contain branded, generic, or contextual anchors rather than forced keywords. -
Review the linking domain’s overall quality
Domains with thin content, excessive outbound links, or no real audience often exist solely to manipulate rankings. These domains frequently appear across multiple spam networks. -
Check topical relevance between sites
A backlink from an unrelated niche—such as a gambling or adult site linking to a medical or corporate website—raises a red flag, especially when repeated. -
Look for patterns, not isolated links
One bad link rarely causes damage. Toxicity usually appears in clusters, which is why pattern recognition is essential.
At Nofal SEO, toxic backlink identification is never automated-only. Each suspicious link is reviewed manually to prevent accidental disavowal of neutral or beneficial links—something that protects long-term SEO growth.
What Is a Disavowal File?
A disavowal file is a technical document submitted to Google that lists backlinks you want ignored during ranking evaluation. In the context of How to disavow malicious links, this file serves as your formal request to exclude harmful external signals from your website’s link profile. It does not delete links; instead, it instructs Google’s algorithms to discount them.
From a technical SEO standpoint, the disavowal file supports link profile correction and penalty recovery workflows. Its accuracy is critical because any mistake—such as disavowing good domains—can permanently reduce your site’s authority. This is why disavowal files should be created cautiously and reviewed thoroughly before submission.
Understanding the structure and rules of a disavowal file is essential before using it.
-
The file must follow strict formatting rules
It must be a plain text (.txt) file encoded in UTF-8 or ASCII. Each line should contain either a full URL or a domain-level directive. -
Domain-level disavowal is often safer
When an entire domain is spammy, disavowing the whole domain is more effective than listing individual URLs that may change over time. -
Comments can be added for documentation
Lines starting with “#” are ignored by Google but help document reasoning, outreach attempts, or categorization. -
One incorrect line can reduce effectiveness
Typos, incorrect syntax, or broken URLs can cause Google to ignore parts of the file, which is why validation is important.

How Do You Disavow Backlinks?
Disavowing backlinks is a multi-stage SEO process that requires preparation, analysis, and precision. When executing How to disavow malicious links, the actual submission step is only the final phase. Most of the work happens beforehand during auditing, classification, and decision-making.
From an operational SEO perspective, backlink disavowal supports penalty resolution and link risk mitigation. Rushing into the process without proper analysis can result in over-disavowal, which weakens your site’s authority rather than protecting it.
To disavow backlinks correctly, each step must be followed carefully.
-
Conduct a full backlink audit first
Collect backlink data from reliable sources, consolidate it, and remove duplicates. This creates a complete view of your link profile. -
Classify links into safe, suspicious, and toxic categories
This step prevents emotional or tool-driven decisions and ensures only genuinely harmful links are targeted. -
Attempt manual link removal where possible
Outreach demonstrates effort and may eliminate the need for disavowal entirely for some links. -
Create and submit the disavow file correctly
Once finalized, upload the file through Google Search Console and document the submission date for tracking.
Measuring Your Disavowal’s Impact and Results
Measuring the success of link disavowal is a long-term SEO task that requires patience and accurate interpretation of data. When working on How to disavow malicious links, many site owners make the mistake of expecting immediate ranking improvements, while in reality disavowal focuses on removing negative influence rather than creating instant gains. The true value appears gradually as Google reprocesses ignored links.
From an analytical SEO perspective, disavowal supports ranking stabilization and penalty recovery tracking. The results should be evaluated across multiple metrics, not just keyword positions. Traffic trends, crawl behavior, and manual action status all play a role in determining whether the disavow process was successful.
To properly assess impact, you need to monitor several indicators over time.
-
Track organic traffic trends rather than daily rankings
Traffic recovery often precedes keyword movement. A gradual return of impressions and clicks indicates that Google is reassessing trust signals positively. -
Monitor Google Search Console manual actions
If a manual action was present, its removal is the strongest confirmation that the disavowal worked. -
Observe indexation and crawl behavior
Improved crawl frequency and fewer crawl anomalies suggest restored confidence in the site. -
Allow sufficient time before making conclusions
Disavowal effects may take weeks or months depending on crawl cycles and backlink volume.
What About Good Backlinks?
Not all low-quality-looking backlinks are harmful, and confusing neutrality with toxicity can damage SEO performance. Understanding How to disavow malicious links also means recognizing which links should never be disavowed. Good backlinks—even from small or unknown websites—often contribute to natural link diversity and authority.
From a strategic standpoint, protecting editorial backlinks and relevant contextual links is just as important as removing toxic ones. Over-disavowal reduces link equity and can slow organic growth, especially in competitive niches.
To preserve healthy backlinks, consider the following principles.
-
Evaluate intent rather than metrics alone
A link placed naturally within content is often more valuable than its domain metrics suggest. -
Check referral traffic and engagement signals
Links that send real users provide value even if SEO metrics appear weak. -
Maintain link diversity
A natural backlink profile includes links from various authority levels, formats, and domains. -
Disavow only when risk is proven
If a link is not causing harm, disavowing it may do more damage than good.
How Do I Disavow a Link?
Disavowing a specific link requires precision and careful judgment. When applying How to disavow malicious links, the decision between URL-level and domain-level disavowal is critical. Choosing incorrectly can either leave harmful links active or eliminate beneficial ones unintentionally.
From an implementation perspective, disavowing a link involves link-level risk assessment and Google disavow syntax accuracy. This process should always be part of a broader backlink cleanup strategy rather than an isolated action.
To disavow a single link correctly, follow a structured evaluation process.
-
Determine whether the issue is isolated or domain-wide
If only one page is problematic, URL-level disavowal is safer. If the entire domain is spammy, domain-level disavowal is more effective. -
Ensure the link cannot be removed manually
Disavowal should not replace outreach efforts unless removal is impossible. -
Add the link correctly to the disavow file
Syntax errors can cause Google to ignore the instruction entirely. -
Re-upload the updated file after changes
Google replaces previous files, so updates must always include the full list.
How to Remove Toxic Links?
Removing toxic links is always preferable to disavowing them because it eliminates the problem at its source. In the context of How to disavow malicious links, link removal represents the proactive step before relying on Google’s disavow mechanism.
From an SEO operations standpoint, toxic link removal supports clean backlink profiles and manual action reconsideration. Even if removal attempts fail, documenting them is essential for transparency.
Effective toxic link removal follows a clear process.
-
Identify the webmaster or site owner accurately
Contact information is often found through WHOIS data or website contact pages. -
Use professional and non-threatening outreach messages
Aggressive or accusatory language reduces cooperation rates. -
Track all outreach attempts carefully
Documentation is valuable if a reconsideration request is needed. -
Avoid paying for link removals
Paid removals may violate Google’s guidelines and encourage further exploitation.
How Do I Remove an Unwanted Link?
Unwanted links are not always malicious but may still require removal due to branding, accuracy, or outdated content. When applying How to disavow malicious links, it’s important to distinguish between SEO risk and reputational concerns.
From a cleanup perspective, unwanted link removal involves link negotiation and content accuracy management. The goal is to resolve issues without escalating to disavowal unless necessary.
Key considerations for removing unwanted links include:
-
Clarify the reason for removal in outreach
Clear explanations increase the likelihood of cooperation. -
Request anchor text modification when removal isn’t possible
Adjusting anchor text can reduce SEO risk without full removal. -
Follow up professionally if there’s no response
Multiple polite follow-ups are often required. -
Escalate to disavowal only if removal fails
Disavowal remains the final option, not the first.
Should You Disavow Spam Links?
Not every spam-looking link requires disavowal. Understanding How to disavow malicious links includes knowing when not to intervene. Google’s algorithms are capable of ignoring many low-quality links automatically.
From an SEO risk management perspective, unnecessary disavowal can weaken your backlink profile. The decision should be based on scale, intent, and impact rather than appearance alone.
Use the following criteria to decide whether spam links need action.
-
Assess volume and growth rate
A sudden spike in spam links may indicate a negative SEO attack. -
Evaluate anchor text manipulation
Spam links with aggressive commercial anchors are higher risk. -
Check correlation with ranking drops
If no negative impact is visible, disavowal may not be required. -
Disavow only when risk outweighs benefit
Conservative action often produces safer long-term results.
Causes of Malicious Links or Broken Links
Malicious and broken links arise from multiple technical and competitive factors. Understanding How to disavow malicious links requires identifying their root causes to prevent recurrence. From an SEO diagnostics standpoint, these issues are often linked to negative SEO, expired domains, or poor-quality historical link building.
Common causes include:
-
Negative SEO campaigns
Competitors may intentionally point spam links to your site. -
Website hacking or injected links
Compromised websites often distribute malicious backlinks unknowingly. -
Legacy black-hat SEO practices
Old link-building campaigns can continue to harm a site years later. -
Domain changes and expired pages
Broken links often result from structural changes or deleted content.
How to Fix 404 Not Found Errors
404 errors negatively affect both user experience and crawl efficiency. While addressing How to disavow malicious links, fixing broken links helps preserve authority flow and trust signals. From a technical SEO angle, 404 resolution supports crawl optimization and internal link integrity.
Effective solutions include:
-
Implementing 301 redirects for valuable URLs
Redirects preserve link equity and user experience. -
Updating internal links pointing to deleted pages
This prevents crawl waste and navigation issues. -
Removing obsolete external references
Outdated links should be cleaned or redirected. -
Monitoring errors regularly through Search Console
Continuous monitoring prevents accumulation of broken links.
How to Check Malicious Links on Your Website
Regular backlink monitoring is essential for early threat detection. Applying How to disavow malicious links starts with identifying risks before they escalate. From an operational SEO standpoint, link checking supports preventive SEO defense and profile stability.
Effective monitoring includes:
-
Running scheduled backlink audits
Monthly or quarterly audits help catch anomalies early. -
Analyzing anchor text changes
Sudden shifts often signal manipulation. -
Tracking new referring domains
Unfamiliar domains should be reviewed manually. -
Comparing data across multiple tools
Cross-validation reduces blind spots.
Broken Link Analysis
Broken link analysis focuses on identifying links that no longer pass value. When combined with How to disavow malicious links, it ensures authority is not wasted or misdirected. From a structural SEO perspective, broken link analysis supports link equity preservation and site health optimization.
Key analysis steps include:
-
Crawling internal and external links
This reveals dead links and redirect chains. -
Prioritizing high-value broken links
Pages with inbound authority should be fixed first. -
Replacing or redirecting broken URLs
This restores usability and SEO value. -
Documenting recurring patterns
Patterns indicate structural or content issues.
Steps to Disavow Malicious Links
Disavowing malicious links requires a structured and disciplined approach. The foundation of How to disavow malicious links lies in process—not shortcuts. From an execution standpoint, this supports safe SEO recovery and algorithm compliance.
The correct steps include:
-
Performing a comprehensive backlink audit
All data must be consolidated and reviewed. -
Classifying links based on risk level
This prevents accidental disavowal of safe links. -
Attempting removal before disavowal
Outreach demonstrates best practice compliance. -
Creating and submitting a validated disavow file
Accuracy and documentation are critical.
Why Disavowing Malicious Links Is Important for SEO
Disavowing malicious links protects your website’s long-term visibility and credibility. Understanding How to disavow malicious links allows businesses to safeguard their rankings against penalties, negative SEO, and algorithmic suppression.
From a strategic SEO viewpoint, disavowal supports trust restoration and sustainable growth, ensuring that rankings are built on legitimate authority rather than distorted signals.
Key reasons include:
-
Preventing manual and algorithmic penalties
Early intervention reduces long-term damage. -
Maintaining a clean and natural link profile
This supports consistent ranking performance. -
Protecting brand reputation and trust signals
Malicious links can affect perception beyond SEO. -
Ensuring long-term SEO stability
Disavowal is a defensive investment, not a quick fix.
Do you need a consultation about this topic?
Contact on WhatsApp